In mobile personal emergency response systems (mPERS), reliable connectivity is as vital as the device itself. These solutions must send SOS alerts instantly, share precise location data, and stay connected for years on a single charge.
That’s why choosing the right cellular IoT network — LTE-M or NB-IoT — directly impacts both performance and user safety.
According to GSMA Intelligence, over 5.5 billion IoT connections will rely on LTE-M and NB-IoT by 2030, making these technologies the global backbone for telecare and personal safety devices.
Takeaway: Network selection determines not only device reliability but also user protection in real emergencies.
How Network Choice Affects mPERS Device Deployment
Selecting the right IoT connectivity option isn’t only about the device’s operation; it directly impacts deployment efficiency, maintenance, and long-term scalability.
Understanding the infrastructure required for LTE-M and NB-IoT networks will help determine the best-fit solution based on geographical region, target market, and expected device usage.
1. Deployment Considerations: Carrier and Network Availability
Before launching any mPERS device, ensuring carrier support and network availability in the target regions is crucial. LTE-M, with its broader deployment footprint across 4G LTE networks, enjoys much wider global availability, especially in regions like North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
In contrast, NB-IoT networks are still in the expansion phase, and regional coverage may vary, particularly in rural or remote areas where IoT connectivity is paramount.
As carriers continue to phase out 2G and 3G, both LTE-M and NB-IoT are expected to grow rapidly over the next 5 years, with NB-IoT forecasted to hit 3 billion connections by 2030 (Source: GSMA Intelligence). For mPERS providers, this means greater confidence in NB-IoT’s long-term viability, particularly in the context of static devices, smart meters, and rural applications.
Takeaway: Evaluate network availability and future-proof your deployment by selecting networks with strong regional support.
2. Scalability and Future-Readiness
As the IoT landscape rapidly evolves, your choice of IoT network needs to align with future trends. 5G technologies promise unprecedented speeds and efficiency, but LTE-M and NB-IoT will still play a significant role for the next decade. Specifically, NB-IoT offers substantial scalability due to its ability to support millions of low-power devices within a small coverage area, which is beneficial for smart cities and large-scale infrastructure.
Moreover, with 5G Massive IoT coming online in the near future, both LTE-M and NB-IoT will serve as critical building blocks for next-gen IoT solutions, ensuring seamless transition between 4G and 5G networks. For manufacturers and developers of mPERS devices, adopting dual-mode modules today provides immediate access to these evolving networks, ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
Takeaway: Prepare for the future by selecting scalable IoT networks that integrate seamlessly with 5G as it becomes more widespread.
A Closer Look at IoT Device Use Cases for mPERS
Understanding how these networks perform in real-world IoT use cases will guide the design and development of mPERS devices. Let’s explore some specific applications where LTE-M and NB-IoT shine.
1. Urban Lone-Worker Safety Devices
In fast-paced urban environments, LTE-M excels. It provides continuous connectivity for mobile safety wearables, whether worn by field staff, security personnel, or healthcare workers. These workers often need to stay in constant contact with their monitoring stations or teams for updates, location tracking, and emergency response. The high data throughput and voice capabilities make LTE-M the optimal choice for these scenarios.
Additionally, with 5G integration, LTE-M supports enhanced capabilities for edge computing and real-time data analysis, which is critical for urban smart safety initiatives.
2. Rural IoT Solutions
On the other hand, NB-IoT shines in rural areas where coverage is spotty, and infrastructure for traditional mobile networks might be sparse. Its ability to penetrate deep into buildings and its low power consumption make it ideal for fixed monitoring devices such as smart meters, agricultural sensors, or mPERS devices installed in isolated locations. This technology allows devices to run for years on minimal battery power, even in remote regions.
In fact, NB-IoT’s global market is expected to grow significantly, especially in areas like agriculture, energy, and remote healthcare, where cost-effective and energy-efficient solutions are critical.
Takeaway: LTE-M is ideal for urban environments, while NB-IoT excels in rural, fixed-installation use cases.

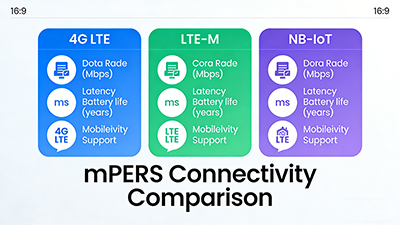
Key Metrics for Selecting the Right IoT Network for mPERS
When evaluating LTE-M and NB-IoT for mPERS devices, it’s important to consider specific performance metrics, including:
| Metric | LTE-M | NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Data Speed | Up to 1 Mbps | Up to 250 Kbps |
| Mobility | High (supports roaming) | Low (fixed installations) |
| Battery Life | 5–10 years | 7–12 years |
| Network Coverage | Broad (urban/suburban) | Deep indoor/rural |
| Voice Support | Yes (VoLTE) | No |
| Deployment Cost | Medium to high | Low to medium |
Battery Life and Network Coverage are two crucial metrics for mPERS device manufacturers. While NB-IoT outperforms in terms of battery longevity, LTE-M offers better coverage and mobility, which could be a deciding factor depending on the device’s purpose.
How Eview’s Dual-Mode Solution Enhances mPERS Performance
Choosing the right IoT network can be daunting, but Eview’s dual-mode mPERS devices ensure that your solution remains flexible and adaptive, allowing seamless switching between LTE-M and NB-IoT networks based on device location, application requirements, and availability.
With Eview’s dual-mode capabilities, you gain:
- Seamless connectivity: Enjoy uninterrupted service, no matter where the device is located.
- Future-proof performance: Dual-mode mPERS devices ensure long-term viability in both 4G and 5G environments.
- Global coverage: Reduce concerns about network outages or lack of carrier support, especially when traveling across regions.
By offering OEM/ODM customization and integration support, Eview guarantees that your devices will meet regional connectivity demands while providing high levels of security, efficiency, and scalability.
Takeaway: Eview’s dual-mode solutions ensure reliable, future-ready connectivity across the globe.
Industry Trends: IoT and 5G Integration
As 5G begins to roll out globally, it will enhance the capacity of NB-IoT and LTE-M, particularly in IoT-heavy sectors like healthcare, logistics, and agriculture. 5G Massive IoT will allow for ultra-low latency, increased device density, and advanced edge computing, making it even easier for mPERS devices to perform complex real-time operations.
Already, 2025 projections suggest the global IoT device market will exceed $300 billion, driven largely by applications like mPERS, telecare, and smart cities. For IoT device manufacturers, ensuring your products are compatible with both 4G and 5G networks is paramount.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Network for Your mPERS Device
In conclusion, choosing between LTE-M and NB-IoT for your mPERS devices is about understanding your application’s needs. Both networks are critical components of the growing IoT ecosystem, but their strengths vary depending on mobility, coverage, and power consumption.
For urban and mobile applications, LTE-M offers faster speeds, voice capabilities, and broader coverage. For more static and low-power applications, NB-IoT provides better battery life and deep indoor coverage.
And with Eview’s dual-mode solution, you get the best of both worlds, ensuring that your devices are always connected, secure, and future-proof.
FAQ
1. Why choose LTE-M over NB-IoT?
LTE-M is better for applications that require mobility and voice capabilities, such as wearable safety devices.
2. Can NB-IoT be used in urban environments?
Yes, but LTE-M generally provides better coverage in urban areas with higher mobility needs.
3. What are the key factors for choosing between these networks?
Consider battery life, coverage, mobility, and whether the device requires two-way communication (for voice).
4. Will 5G replace LTE-M and NB-IoT?
No, LTE-M and NB-IoT will continue to be integral to 5G Massive IoT deployments due to their low-power requirements.
5. Will LTE-M and NB-IoT remain relevant in the 5G era?
Absolutely. Both technologies are integral to the 5G Massive IoT roadmap and will be supported well into the next decade, ensuring stability and longevity for connected devices.
About Eview