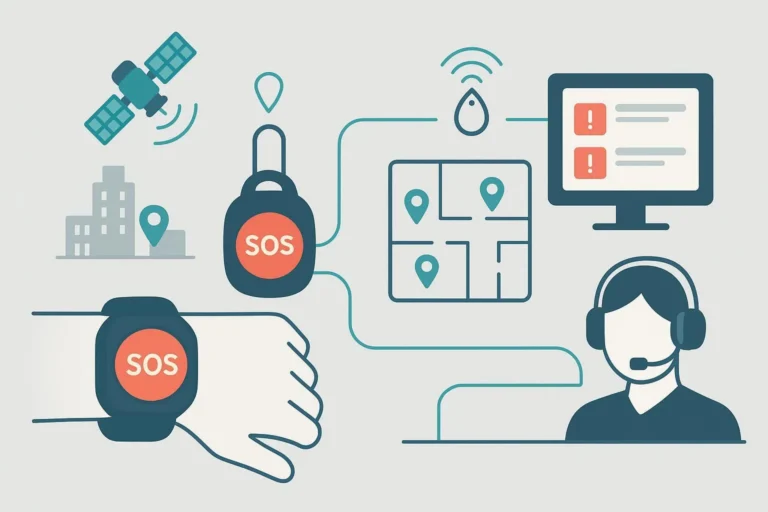
How IoT healthcare devices are transforming remote patient monitoring and advancing patient safety across global healthcare systems.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into healthcare—known as medical IoT or IoMT—is reshaping how medical professionals monitor, diagnose, and support patients.
With remote patient monitoring (RPM) technologies, healthcare providers can track vital signs and safety indicators in real time, empowering better decisions and proactive care.
As populations age and chronic conditions rise, connected healthcare devices are becoming essential tools for ensuring personal safety, reducing hospital visits, and improving patient outcomes.
What Is IoT in Healthcare?
The rise of IoT healthcare devices marks a key shift in how medical systems operate. Through interconnected sensors and cloud-enabled data platforms, medical IoT connects patients, clinicians, and systems into one intelligent network. This foundation enables remote patient monitoring on a scale previously impossible, improving efficiency and preventive care through constant visibility into patient health.
The Definition and Core Concept of IoMT
IoT in healthcare refers to a network of interconnected sensors, wearable devices, and monitoring systems that collect and exchange medical data through the internet.
This ecosystem is called the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
How IoT Connects Devices, Data, and Patients
Each connected device transmits data—such as heart rate, blood glucose, or motion activity—to cloud platforms where clinicians can analyze patterns and detect anomalies.
This real-time feedback loop bridges patients, caregivers, and medical institutions in a unified data-driven ecosystem.

Fundamentals of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
At the heart of remote patient monitoring lies a structured IoT ecosystem built on device connectivity, real-time data, and actionable insights. These IoT healthcare devices capture vital health information and deliver it directly to care teams. By combining sensing, transmission, and analysis, medical IoT allows clinicians to make informed decisions faster, minimizing the delay between symptom detection and response.
The Four Core Components of RPM Systems
- Sensing devices – Collect patient vitals (ECG, SpO₂, blood pressure).
- Data transmission modules – Send data via Wi-Fi, LTE, or NB-IoT.
- Cloud-based analytics – Aggregate and analyze data streams.
- Clinical dashboards – Enable doctors to review alerts and trends.
From Hospital-Centric to Home-Based Models
Traditionally, patient monitoring occurred only in hospitals.
Now, with IoT-enabled RPM, patients can be safely monitored at home, reducing hospital congestion and enhancing comfort.
Core IoT Healthcare Devices Used in RPM
The diversity of IoT healthcare devices underpins the strength of modern remote patient monitoring. From wearable biosensors to home-based medical hubs, these tools continuously collect and share critical information. Integrated through medical IoT frameworks, these devices ensure accurate health insights while promoting consistent communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Wearables and Biosensors
Devices such as smartwatches, ECG patches, and wearable oximeters continuously record key vital signs and transmit them securely to cloud platforms.
Smart Home Medical Devices
Connected blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and thermometers automatically sync results with healthcare portals—minimizing manual entry errors.
Safety-Oriented Environmental Sensors
Sensors placed in living environments detect motion, humidity, or falls—providing a layer of personal safety for elderly and vulnerable users.
Real-Time Data and Clinical Insights
One of the greatest contributions of medical IoT is its ability to deliver continuous, real-time data streams. This constant flow from IoT healthcare devices allows doctors to detect anomalies as they occur, supporting predictive interventions in remote patient monitoring programs. By transforming static records into live health intelligence, IoT reshapes how care decisions are made.
Continuous Data Flow
IoT healthcare devices provide 24/7 data streams instead of intermittent clinical visits, allowing early detection of irregularities.
Predictive Analytics in Remote Care
Machine learning models can identify subtle trends, predicting potential risks such as heart failure or respiratory decline before symptoms worsen.
According to Healthcare IT News (2024), hospitals using predictive IoT systems reduced emergency admissions by up to 25%.
Personal Safety Applications of IoT
Beyond clinical monitoring, IoT healthcare devices strengthen personal safety through automatic alerts and environmental awareness. In remote patient monitoring systems, fall detection sensors and SOS wearables can instantly connect patients to caregivers. Such medical IoT solutions reduce response times and enable safer independent living for vulnerable individuals.
Fall Detection and Emergency Alerts
Wearable SOS devices and motion sensors automatically detect falls or abnormal inactivity, instantly alerting caregivers or emergency services.
Geo-Fencing and Location Tracking
GPS-enabled medical IoT devices provide real-time positioning for patients with dementia or cognitive impairments, ensuring timely rescue and safety.

Improving Chronic Disease Management
Chronic disease care has evolved through remote patient monitoring powered by IoT healthcare devices. Patients with conditions such as diabetes or heart disease benefit from continuous feedback loops and trend analysis. These medical IoT systems help clinicians adjust treatments in real time, enabling proactive care rather than reactive crisis management.
Chronic Care Through Continuous Monitoring
For patients with diabetes or cardiovascular disease, connected devices enable long-term tracking of glucose levels, blood pressure, and physical activity.
Personalized Treatment Adjustments
IoT platforms integrate patient data over time to provide personalized medication adjustments and preventive alerts—reducing complications and improving outcomes.
Integration with Clinical Workflows and Telehealth
For healthcare providers, the success of IoT healthcare devices depends on seamless integration with clinical systems. Medical IoT connects data directly into EHR and telehealth platforms, allowing remote patient monitoring to function as an extension of the hospital’s ecosystem. This synchronization enhances accuracy, reduces manual data entry, and supports continuous digital care.
EHR and Teleconsultation Synergy
Data from RPM systems seamlessly integrates into Electronic Health Records (EHR), supporting teleconsultations with up-to-date patient information.
Interoperability in Connected Health
Standardized APIs and protocols (HL7, FHIR) ensure data can move securely between devices, hospitals, and telehealth applications—eliminating silos.
Benefits for Patients and Healthcare Providers
The measurable impact of IoT healthcare devices extends to cost reduction, improved engagement, and better outcomes. Remote patient monitoring supported by medical IoT technologies enhances early detection and reduces hospital visits. Both patients and healthcare providers gain efficiency, transparency, and confidence in the care process through connected insights.
Quantitative ROI and Adoption Data
| Metric / Benefit | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare organizations using or exploring RPM | 88% | Consumer Technology Association (CTA, 2023) |
| Providers planning to expand RPM investments | 68% | CTA, 2023 |
| Global medical IoT market size (2022) | USD 108.4 Billion | Emergen Research |
| Expected CAGR (2023–2030) | ~17.5% | Emergen Research |
| Reduction in hospital readmissions via IoT | Up to 30% | McKinsey HealthTech Survey |
Key Takeaways
- Operational efficiency – Real-time alerts reduce response times.
- Cost reduction – RPM helps save an estimated $200–$400 per patient/month in chronic care programs.
- Patient empowerment – Patients actively participate in managing their health metrics.
Challenges and Security Considerations
While IoT healthcare devices deliver clear advantages, medical IoT also introduces challenges in security and interoperability. Managing sensitive data within remote patient monitoring frameworks requires robust encryption, standardized protocols, and regulatory compliance. These safeguards protect patient privacy while preserving the integrity of digital health ecosystems.
Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Handling sensitive health data requires full compliance with HIPAA (U.S.) and GDPR (EU). Encrypted data channels and strict access controls are mandatory for any IoT healthcare deployment.
Device Interoperability and Technical Barriers
Different device vendors often use proprietary protocols. The lack of interoperability can hinder scalability.
Adopting open standards (e.g., IEEE 11073, FHIR) is essential for integration.
![]()
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of remote patient monitoring is deeply tied to innovations in IoT healthcare devices and intelligent data processing. Emerging medical IoT trends—such as AI-based analytics, 5G networks, and edge computing—will make patient monitoring more precise and responsive. These advances point toward a future where healthcare becomes fully connected, predictive, and preventive.
AI and Predictive Monitoring
AI algorithms analyze IoT data to forecast patient deterioration, enabling proactive intervention. For example, AI-powered RPM can predict a potential heart failure up to 72 hours in advance.
5G and Edge Computing for Healthcare IoT
5G enables ultra-low-latency connections for high-frequency data transmission, while edge computing processes information locally—reducing delays in emergency response.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become an indispensable component of modern healthcare. By connecting devices, patients, and data ecosystems, IoT healthcare devices are transforming remote patient monitoring and personal safety management. Through predictive analytics, interoperability, and patient-centered design, medical IoT is not only improving clinical efficiency but also building a safer, smarter, and more responsive healthcare environment for the future.
About Eview

FAQ: IoT in Remote Patient Monitoring and Personal Safety
1. What are IoT healthcare devices, and how are they used in remote patient monitoring?
IoT healthcare devices are connected tools such as wearable sensors, smart blood pressure monitors, and glucose trackers that collect real-time patient data.
In remote patient monitoring (RPM), these devices continuously send vital information—like heart rate, oxygen levels, and temperature—to healthcare platforms.
Clinicians can review these metrics remotely, improving early intervention and reducing hospital readmissions.
2. How does IoT improve personal safety for patients at home?
IoT improves personal safety through real-time alerts, fall detection, and emergency response systems.
For example, elderly patients wearing SOS-enabled devices can automatically notify caregivers during an accident.
Geo-fencing technologies in medical IoT trackers also ensure location-based monitoring for patients with cognitive conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
3. What are the key benefits of remote patient monitoring using IoT devices?
The main benefits include:
- Continuous care: 24/7 monitoring instead of periodic hospital checkups.
- Cost efficiency: Studies show up to 30% reduction in hospital readmissions through IoT-based RPM programs.
- Personalization: Data-driven treatment adjustments improve outcomes.
- Accessibility: Patients in remote regions gain access to quality healthcare.
These benefits make IoT healthcare devices essential for value-based, outcome-oriented care models.
4. Is medical IoT data secure and compliant with regulations?
Yes—when properly implemented. Healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA (U.S.), GDPR (EU), and local data protection laws. Security measures include:
- End-to-end encryption of patient data.
- Multi-factor authentication for clinicians.
- Regular vulnerability testing of IoT platforms.
Modern IoT healthcare solutions are designed with these safeguards to ensure both safety and compliance.
5. What challenges does IoT face in healthcare adoption?
Future trends point toward:
- AI-driven predictive monitoring is capable of anticipating medical emergencies up to 72 hours in advance.
- Edge computing for faster local processing of health data.
- Wearable miniaturization for more discreet and comfortable monitoring.
- Integration with telehealth platforms, creating seamless hybrid care ecosystems.
The medical IoT market, valued at over USD 108 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.5% through 2030 (Emergen Research).